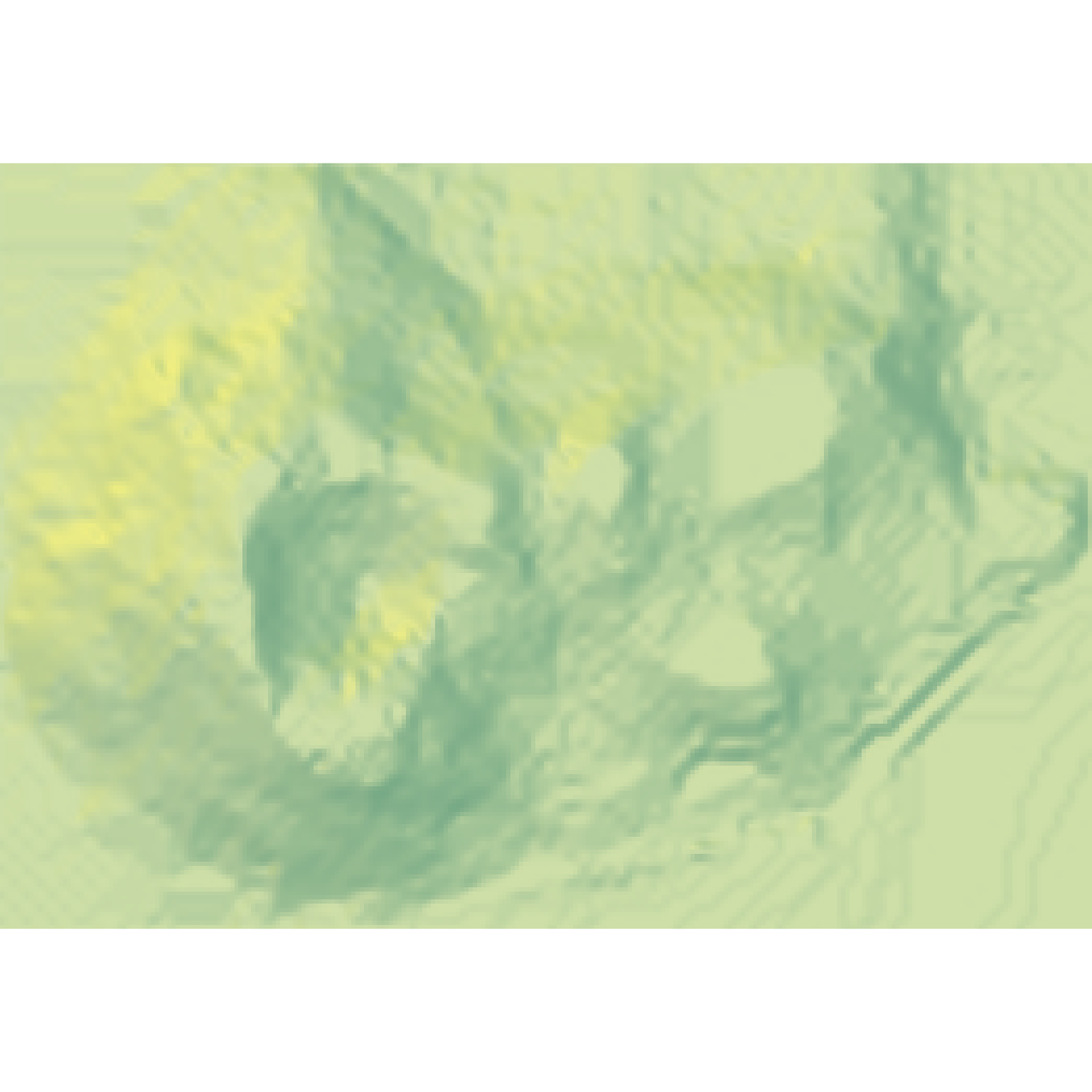
Resizes a matrix (preserving contents) by specifying the desired output dimensions or a scaling factor.
resize_matrix(
heightmap,
scale = 1,
width = NULL,
height = NULL,
method = "bilinear"
)Arguments
- heightmap
The elevation matrix.
- scale
Default `0.5`. The amount to scale down the matrix. Scales using bilinear interpolation.
- width
Default `NULL`. Alternative to `scale` argument. The desired output width. If `width` is less than 1, it will be interpreted as a scaling factor– e.g. 0.5 would halve the resolution for the width.
- height
Default `NULL`. Alternative to `scale` argument. The desired output width. If `height` is less than 1, it will be interpreted as a scaling factor– e.g. 0.5 would halve the resolution for the height.
- method
Default `bilinear`. Method of interpolation. Alteratively `cubic`, which is slightly smoother, although current implementation slightly scales the image.
Examples
#Reduce the size of the monterey bay dataset by half
if(run_documentation()) {
montbaysmall = resize_matrix(montereybay, scale=0.5)
montbaysmall %>%
sphere_shade() %>%
plot_map()
}
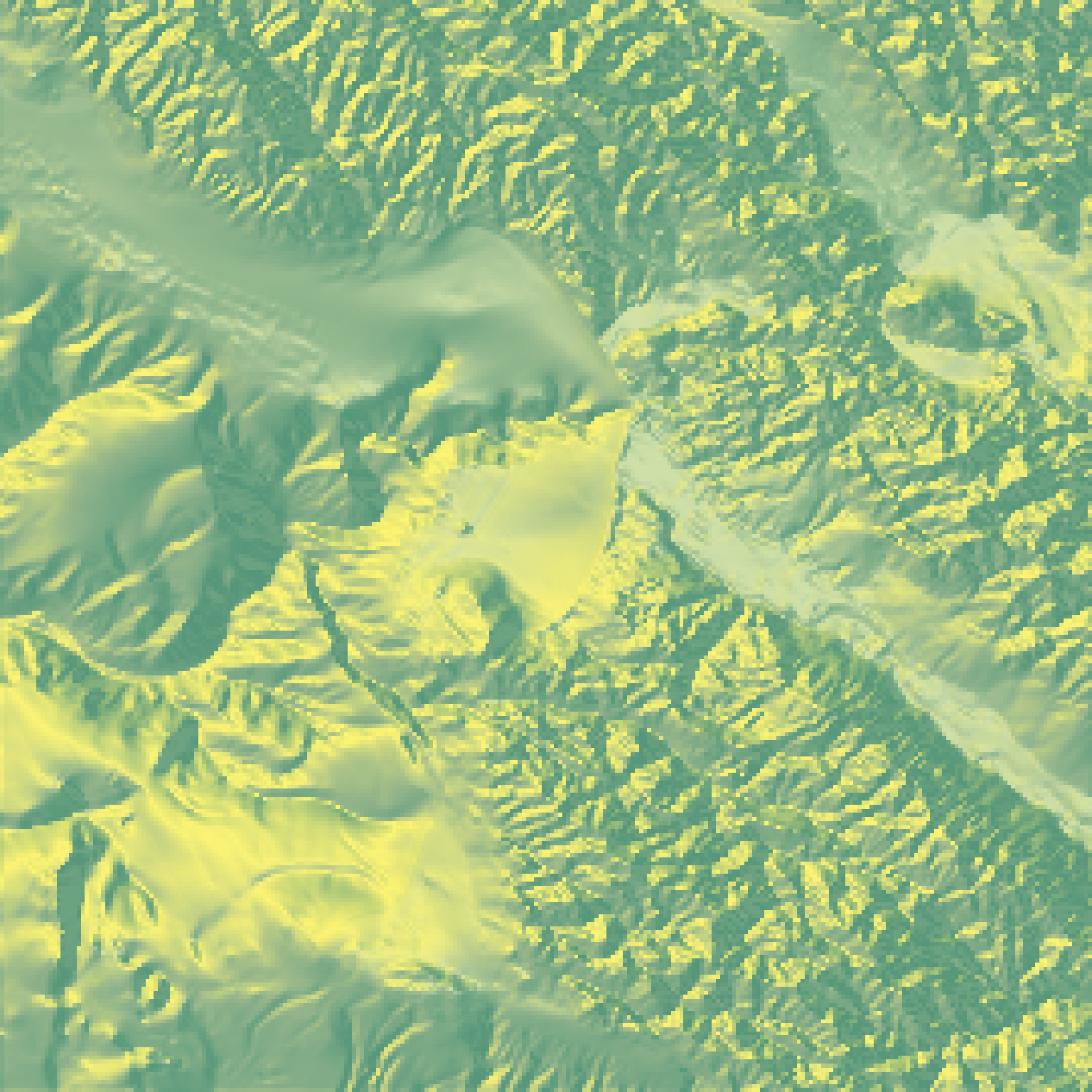 if(run_documentation()) {
#Reduce the size of the monterey bay dataset from 540x540 to 100x100
montbaysmall = resize_matrix(montereybay, width = 100, height = 100)
montbaysmall %>%
sphere_shade() %>%
plot_map()
}
if(run_documentation()) {
#Reduce the size of the monterey bay dataset from 540x540 to 100x100
montbaysmall = resize_matrix(montereybay, width = 100, height = 100)
montbaysmall %>%
sphere_shade() %>%
plot_map()
}
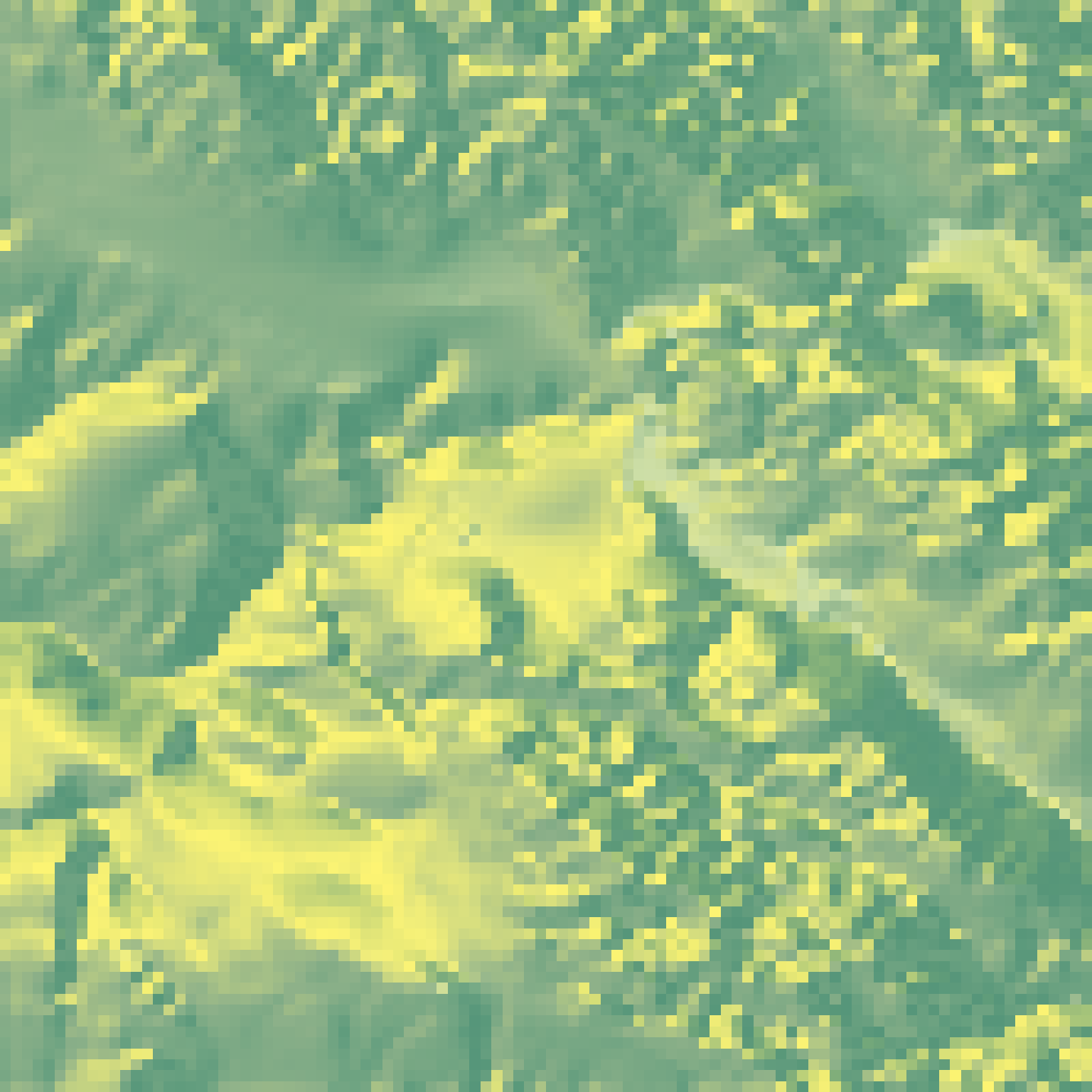 if(run_documentation()) {
#Increase the size of the volcano dataset 3x
volcanobig = resize_matrix(volcano, scale=3)
volcanobig %>%
sphere_shade() %>%
plot_map()
}
if(run_documentation()) {
#Increase the size of the volcano dataset 3x
volcanobig = resize_matrix(volcano, scale=3)
volcanobig %>%
sphere_shade() %>%
plot_map()
}
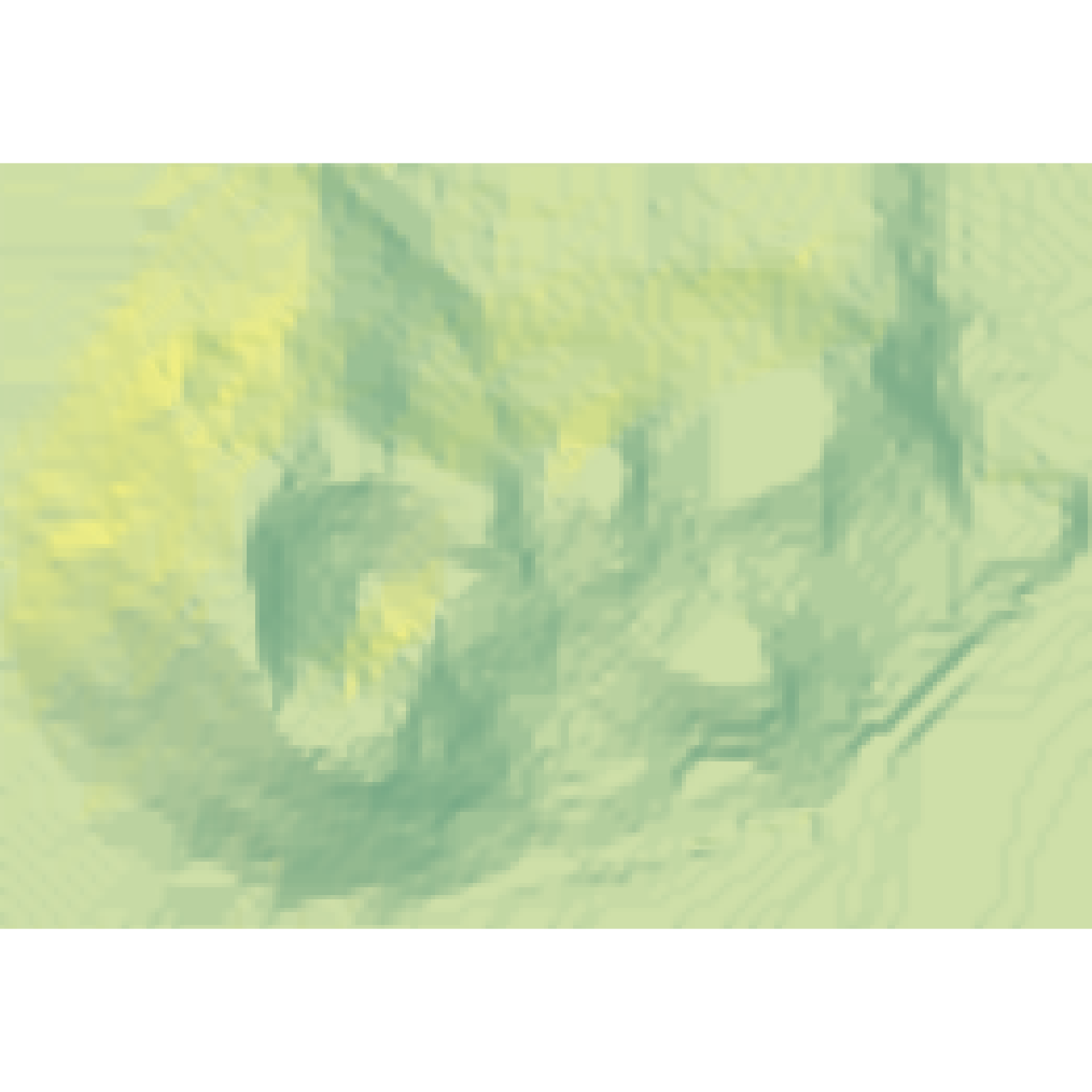 if(run_documentation()) {
#Increase the size of the volcano dataset 2x, using cubic interpolation
volcanobig = resize_matrix(volcano, scale=3, method="cubic")
volcanobig %>%
sphere_shade() %>%
plot_map()
}
if(run_documentation()) {
#Increase the size of the volcano dataset 2x, using cubic interpolation
volcanobig = resize_matrix(volcano, scale=3, method="cubic")
volcanobig %>%
sphere_shade() %>%
plot_map()
}